Kitakami Mountains on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
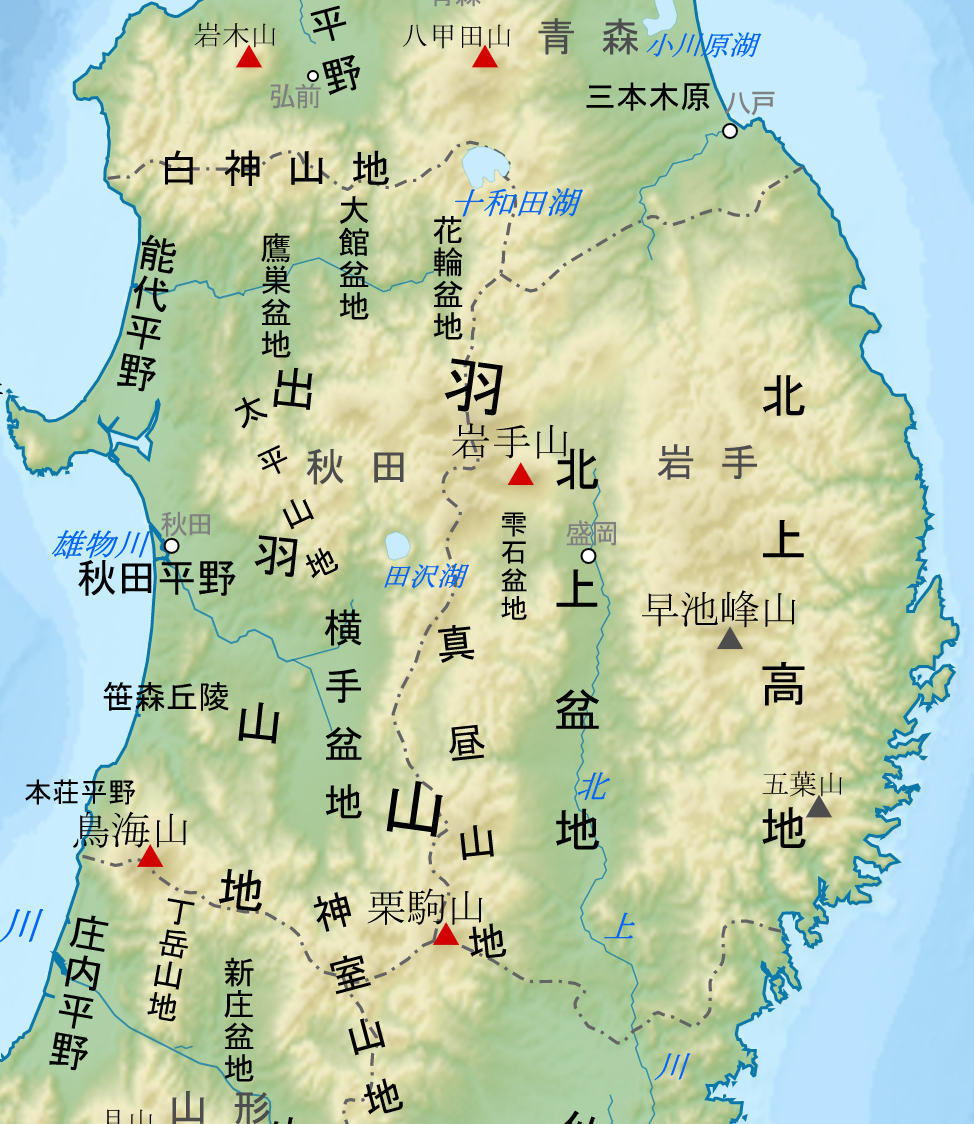 is a mountain range in northeastern
is a mountain range in northeastern Kitakami Mountains
''Encyclopedia Britannica’ The range extends for from the southern border of
 is a mountain range in northeastern
is a mountain range in northeastern Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island se ...
, in the Tōhoku region
The , Northeast region, or consists of the northeastern portion of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. This traditional region consists of six prefectures (''ken''): Akita, Aomori, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi, and Yamagata.
Tōhoku reta ...
of northern Japan.''Encyclopedia Britannica’ The range extends for from the southern border of
Aomori Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan in the Tōhoku region. The prefecture's capital, largest city, and namesake is the city of Aomori. Aomori is the northernmost prefecture on Japan's main island, Honshu, and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the eas ...
in the north to the northern border of Miyagi Prefecture in the south, and are bordered by the Kitakami River
The is the fourth largest river in Japan and the largest in the Tōhoku region. It is long and drains an area of . page 793 It flows through mostly rural areas of Iwate and Miyagi Prefectures. The source of the river is the Mount Nanashir ...
valley in the west and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
to the east, with an average width of around .The Kitakami Mountains are thus mostly located within eastern Iwate Prefecture. The range is largely an eroded plateau with a thick granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
bedrock, thus accounting for its other name: . In the north, the mountains are characterized by marine terrace
A raised beach, coastal terrace,Pinter, N (2010): 'Coastal Terraces, Sealevel, and Active Tectonics' (educational exercise), from 2/04/2011or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin,Pira ...
s at an altitude of around 300 meters, whereas in the south, the mountains are drowned to form a deeply indented rias coast.
Geologically, the Kitakami Mountains are Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
formations, divided into northern and southern groups. the southern area has oldest previous Silurian foundation, which was once a shallow sea on the continental margin where the water temperature was high enough for coral growth from the Silurian to the Devonian periods; this region, later collided with the northern Kitakami mountainous area in the early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period, and the whole was penetrated by the granite in various places. Until the Paleogene, the Kitakami Mountains were geologically part of Primorsky region of Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
. About 30 million years to 15 million years ago, the Japanese archipelago separated from the continent and moved to its present position. The Kitakami Mountains around that time was an island, the west side was a shallow sea, and the Ōu Mountains
The are a mountain range in the Tōhoku region of Honshū, Japan. The range is the longest range in Japan and stretches south from the Natsudomari Peninsula of Aomori Prefecture to the Nasu volcanoes at the northern boundary of the Kantō ...
were not yet born. The uplift of the Ōu mountain range began in late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
and the Kitakami Basin was born. The Kitakami Mountains were exposed to erosion for a long time because they were above water from the Cenozoic onwards. In addition, as a result the glacier effects of the last glacial period, the current gentle topography was created.
Mount Hayachine
is the highest mountain in the Kitakami Range, located in the Tōhoku region of northern Honshū, Japan. With an elevation of , it is the second highest in Iwate Prefecture after Mount Iwate. Mount Hayachine is mentioned in ''100 Famous Japane ...
, near the center of the range, is the highest peak at , and supports endemic alpine vegetation.
Notable caves within the Kitakami Mountains include Akkadō and Ryūsendō
is one of Japan's three largest limestone caverns. It is located in the town of Iwaizumi, Iwate Prefecture, in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan.
Ryūsendō has an accessible length of 1200 meters, making it the 62nd longest in Japan; how ...
.
The peaks of the Kitakami mountains include the following:
*Mount Hayachine
is the highest mountain in the Kitakami Range, located in the Tōhoku region of northern Honshū, Japan. With an elevation of , it is the second highest in Iwate Prefecture after Mount Iwate. Mount Hayachine is mentioned in ''100 Famous Japane ...
(早池峰山) 1917 m
*Hashigamidake (階上岳) 739.6 m
*Akkamori (安家森) 1239 m
*Kuromoriyama (黒森山) 837 m
*Goyozan (五葉山)1351 m
*Muroneyama (室根山) 895 m
*Omoriyama (大森山) 750 m
*Tokusenjosan (徳仙丈山) 711 m
*Tatsuganesan (田束山) 512 m
References
*Notes
{{Authority control Mountain ranges of Aomori Prefecture Mountain ranges of Iwate Prefecture Mountain ranges of Miyagi Prefecture